 A computed tomography scan, more commonly referred to as CT or CAT scan, is medical imaging formed through a series of X-ray views taken from different angles, allowing for three-dimensional representations of bodily structures.
University Center Imaging uses the newest in technology, the Siemens SOMATOM Perspective 128-slice CT, to capture the most detailed images of organs, bones and other tissues while offering improved image quality and increased imaging speeds. The special X-ray images are of the slices of bodily structures that doctors are interested in examining more closely. Because of this, CT exams are one of the most commonly performed medical procedures in both hospitals and imaging centers. UCI is highly conscious of the radiation associated with CT scans. Our CT scanner is Low Dose, producing 60% less radiation than other scanners. We are also recognized by ACR for Image Wisely.
A computed tomography scan, more commonly referred to as CT or CAT scan, is medical imaging formed through a series of X-ray views taken from different angles, allowing for three-dimensional representations of bodily structures.
University Center Imaging uses the newest in technology, the Siemens SOMATOM Perspective 128-slice CT, to capture the most detailed images of organs, bones and other tissues while offering improved image quality and increased imaging speeds. The special X-ray images are of the slices of bodily structures that doctors are interested in examining more closely. Because of this, CT exams are one of the most commonly performed medical procedures in both hospitals and imaging centers. UCI is highly conscious of the radiation associated with CT scans. Our CT scanner is Low Dose, producing 60% less radiation than other scanners. We are also recognized by ACR for Image Wisely. 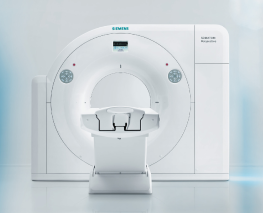
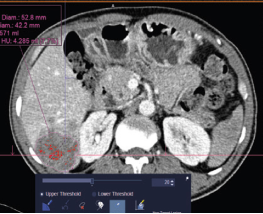

At UCI, we specialize in various types of CT scans, including:
CT Angiography: This minimally invasive medical test helps doctors diagnose and treat a variety of medical conditions. Frequently, a contrast dye is injected through an IV during the CT scan to produce detailed images of your blood vessels and tissues. A CT angiogram helps us determine if a blood vessel is blocked. If it is blocked, the images then allow us to find where the blockage is, as well as how big it is. It also helps us identify aneurysms or plaque buildup. CT angiograms are less invasive than standard angiograms.
CT Urography: An urography is a specialized radiological exam that focuses on evaluating the urinary tract, specifically the kidneys, ureters and bladder. It uses CT technology to produce cross-sectional images of these internal organs, which allows your physician to diagnose conditions and plan a course of action. It’s often used to detect kidney stones or evaluate patients who have blood in their urine.
Low Dose Lung Screening: The American College of Radiology (ACR) has recognized University Center Imaging as a Designated Lung Cancer Screening Center. The best tool for a lung screening is a CT. This provides detailed, cross sectional views and is able to scan the entire chest in about five to ten seconds. The entire lung screening process will take approximately 15 minutes.
Coronary Calcium Scoring: A cardiac CT scan is a non-invasive way of obtaining information about the location and extent of calcified plaque in the coronary arteries—the vessels that supply oxygen-containing blood to the heart wall. Plaque is a build-up of fat and other substances, including calcium, which can, over time, narrow the arteries or even close off blood flow to the heart. The result may be painful angina in the chest or a heart attack. The entire screening process will take approximately 15 minutes.
CT scans are useful in many different medical situations in which diagnostic imagery is needed. CT scans are frequently used to evaluate the brain, spine, neck, abdomen and chest, providing clear images of both soft and hard tissue. These images are also used when you have specific symptoms like pain or dizziness. They can even be helpful in examining the spread of diseases like cancer. Depending on where the CT scan is directed in your body, there are a variety of uses:
Depending on the area of the body being imaged, you may be asked to drink a contrast agent to enhance the pictures that are taken of your body. You will receive special instructions if your exam requires you to consume an oral contrast agent (barium sulfate) in advance or an IV Contrast (iodine injection). Both contrasts serve multiple purposes and help provide valuable information for diagnosing medical problems.